Introduction
Trenching and excavation work are among the most dangerous tasks in the construction industry. One of the primary concerns is trench collapse, which can cause serious injuries or fatalities. To mitigate these risks, trench protection systems, including trench boxes (also known as trench shields), are widely used. However, an ongoing debate in the construction industry is whether job-built trench boxes—trench boxes fabricated on-site—are permissible. This article explores the regulations, safety concerns, and alternatives surrounding job-built trench boxes in construction.
What Are Trench Boxes?
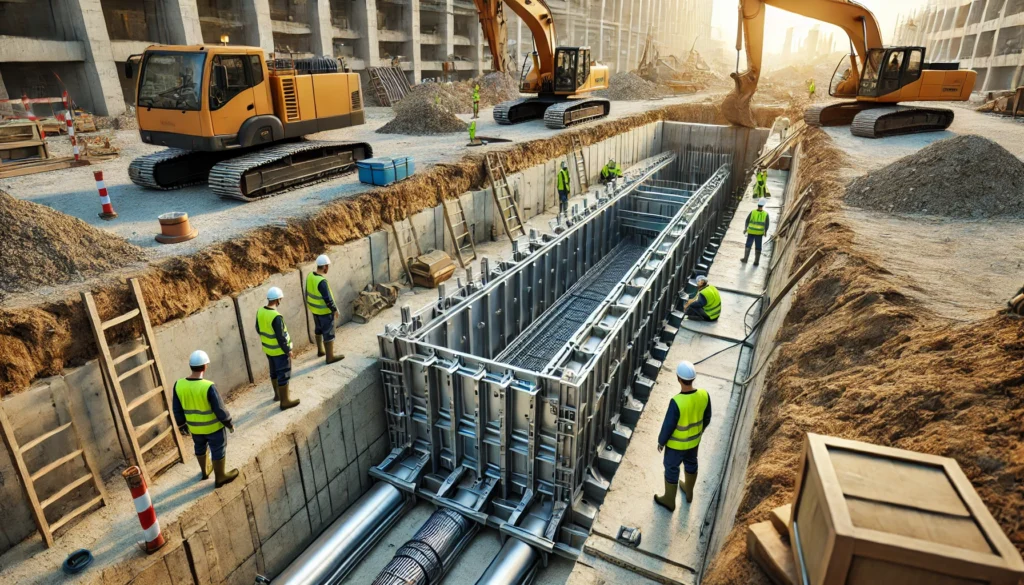
Trench boxes are protective structures designed to prevent soil from caving into an excavation site. They are commonly used in projects involving underground utilities, foundation work, and pipeline installations.
Components of a Trench Box
- Sidewalls: Heavy-duty steel or aluminum panels that provide lateral protection.
- Spreaders: Horizontal bars that maintain the trench box’s shape and adjust for width.
- Lifting points: Reinforced areas for hoisting the box into place with machinery.
Standard vs. Job-Built Trench Boxes
- Standard Trench Boxes: Pre-engineered and manufactured by recognized companies, meeting Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards.
- Job-Built Trench Boxes: Custom-fabricated on-site by workers or contractors, typically to fit specific project needs.
Are Job-Built Trench Boxes Allowed?
OSHA Regulations and Compliance
According to OSHA’s excavation standards (29 CFR 1926.650-652), trench protection systems must be engineered and certified to withstand the expected loads.
- Job-built trench boxes may be allowed, but they must be designed by a registered professional engineer and certified for use.
- Employers are responsible for ensuring that any protective system, including job-built trench boxes, meets strength and safety requirements.
Risks and Safety Concerns
While job-built trench boxes offer flexibility, they also pose significant risks if not properly designed and maintained:
- Structural integrity concerns: Improper welding, weak materials, or incorrect dimensions can lead to collapse.
- Lack of testing and certification: Unlike factory-built trench boxes, job-built versions may not undergo rigorous safety testing.
- Legal liability: If a job-built trench box fails, the company could face OSHA violations, hefty fines, and legal consequences.
Alternatives to Job-Built Trench Boxes
Pre-Engineered Trench Boxes
Manufactured trench boxes undergo strict testing to ensure compliance with safety standards. Benefits include:
- Guaranteed structural integrity
- Certified compliance with OSHA regulations
- Higher durability and reliability
Hydraulic Trench Shoring Systems
For situations where trench boxes are impractical, hydraulic trench shoring systems can be a viable alternative. They offer:
- Adjustable support for various trench widths
- Ease of installation in confined spaces
- Compliance with safety regulations
Trench Sloping and Benching
Instead of using a trench box, contractors may opt for:
- Sloping: Cutting back trench walls at an angle to prevent cave-ins
- Benching: Creating step-like levels along trench walls
These methods are effective in stable soil conditions but may not be suitable for deep excavations or loose soil types.
Best Practices for Trench Safety
Regardless of the trench protection system used, the following safety measures should always be followed:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct daily checks before and after work shifts.
- Worker Training: Educate employees on trench safety and emergency procedures.
- Proper Installation: Ensure trench boxes or alternative systems are correctly placed and maintained.
- Monitoring Soil Conditions: Be aware of environmental factors that could impact trench stability.
Conclusion
While job-built trench boxes are not outright prohibited, their use comes with strict conditions, including engineering approval and OSHA compliance. Given the risks associated with improper fabrication, most contractors prefer pre-engineered trench boxes or alternative safety measures to ensure trenching operations remain safe and compliant.
For construction professionals, investing in certified trench protection systems is the safest and most reliable approach. If you are unsure about your trench safety requirements, consult a professional engineer or refer to OSHA guidelines to avoid violations and protect your workforce.

Andre Cuevas provides career insights, job search strategies, and professional advice to help individuals navigate the job market and achieve their career goals.